
RBI Surprises with 50 bps Repo Cut, CRR Reduction, and Stance Shift to ‘Neutral’
#
6th Jun, 2025
- 3597 Views
NDNC disclaimer: By submitting your contact details or responding to Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited., with an SMS or Missed Call, you authorise Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited and/or its authorized Service Providers to verify the above information and/or contact you to assist you with the purchase and/or servicing
Comments from Mr. Srinivas Rao Ravuri, Chief Investment Officer, Bajaj Allianz Life
Monetary Policy Decision – Proactive and Aggressive Rate Cuts
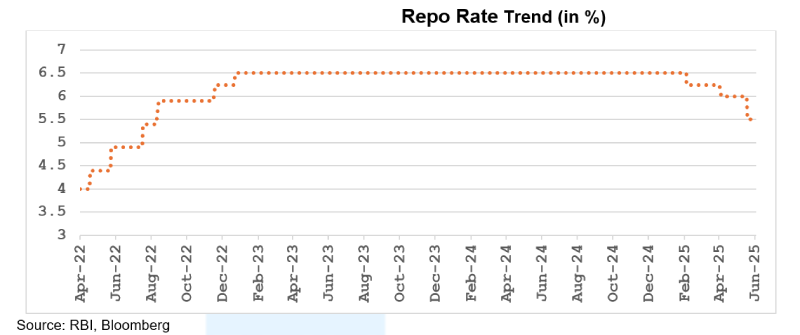
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) met during June 4–6, 2025 and decided to reduce the policy repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.50%, third consecutive cut since February 2025 (Cumulatively 100 bps rate cut), signalling the RBI’s clear intent to frontload support for economic growth, as inflation continues to ease, and global growth concerns linger. Also, in a surprise move, the RBI also decided to reduce CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) to 3% from 4% in four tranches.
Shift in Stance: From Accommodative to Neutral
While reducing the key rates, the MPC also shifted its stance from “accommodative” to “neutral,” to curb any irrational exuberance in the financial markets. The change in stance also indicates that future decisions will depend on incoming data and economic developments and reflects the limited room left for further monetary easing measures.
Liquidity and Market Conditions – CRR Cut by 100 bps
Since January 2025, the RBI has injected Rs. 9.5 lakh crore of durable liquidity into the system, turning a previous liquidity deficit into a surplus. The proposed Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) cut will also release Rs. 2.5 lakh crore into the system by December 2025. This will reduce funding costs for banks and help transmit rate cuts to borrowers.
Inflation Outlook: Benign Trend Continues
Headline CPI inflation dropped to 3.2% in April 2025—the lowest in nearly six years—mainly due to continued softening of food prices. The RBI now forecasts average inflation for FY 2025–26 at 3.7%, down from its earlier estimate of 4.0%. With expectations of a good monsoon and strong crop output, food prices are likely to remain under control. However, the RBI remains watchful of weather-related risks and evolving global trade dynamics.
Growth Momentum Remains Steady Despite Global Uncertainty
India’s GDP growth for FY 2024–25 was recorded at 6.5%, and the RBI expects the same pace to continue in FY 2025–26. The economy showed strength in Q4, with private consumption and investment rising. Agriculture has benefited from strong harvests, and services continue to expand robustly. Industrial recovery remains uneven but is improving. Domestic demand indicators—including consumer goods sales and capital goods production—are showing positive trends.
External Sector: Resilient Amid Global Headwinds
Despite global uncertainty, India’s external sector remains stable. Foreign exchange reserves stood at $691.5 billion as of May 30, 2025, covering more than 11 months of imports. Services exports and remittances remain strong, and though net FDI and FPI flows have moderated, gross FDI continues to rise. Trade remains a concern due to slowing global demand, but free trade agreements may offer upside potential.
Financial System: Healthy and Stable
The health of the banking system remains robust, with strong capital positions, improved asset quality, and high liquidity buffers. NBFCs also maintain healthy balance sheets, although the microfinance segment requires close monitoring. Stress in retail loan segments has reduced, and lenders are tightening credit norms where needed.
Outlook:
Against the market expectations of a 25-bps rate cut, the central bank has decided to front load monetary measures to supports economic growth with 50 bps cut in Repo & 100-bps staggered cut in the CRR. This will result in lower FD rate, lower home and other consumers loans rates, which will stimulate demand in economy. The financial markets have reacted positively to these surprising measures. To curb market enthusiasm the central bank has changed its monetary policy stance to Neutral indicating limited room for further monetary easing. While price stability is its primary goal, the current environment of benign inflation is allowing the RBI to take measures to support growth. The RBI emphasized that both inflation and growth are moving broadly in line with expectations and going forward monetary policy will be carefully calibrated based on evolving domestic and global conditions, with the RBI committed to maintaining stability and promoting sustainable economic progress. We expect, 10yrs G-Sec yield will be range bound between 6.1% to 6.3%. We prefer 5 years corporate bond investment.
Annexure:
CRR – The share of a bank’s total deposits that must be kept with the RBI in cash.
Stance – It gives an indication to the future policy action.
SDF – The rate at which Banks lend to RBI without collateral.
MSF – The rate at which RBI lends (provides emergency liquidity) to Banks.

Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Facebook
Twitter
pintrest
instagram
Whatsapp
Linkedin
More