
GST Rationalisation: A Big Push To Consumption
#
18th Aug, 2025
- 1003 Views
NDNC disclaimer: By submitting your contact details or responding to Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited., with an SMS or Missed Call, you authorise Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited and/or its authorized Service Providers to verify the above information and/or contact you to assist you with the purchase and/or servicing
In his 79th Independence Day address, Prime Minister Narendra Modi unveiled a major overhaul of India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, labeling it a symbolic “Diwali gift” for the common man and the middle class.
The central government has proposed a simplified two-slab structure, comprising “standard” and “merit” rates, with special rates reserved only for select items. Multiple media reports suggest that about 99% of items currently taxed at 12% could move to 5%, and roughly 90% of goods in the 28% bracket may shift to 18%.
This represents a deep dismantling of the current four-slab structure (5%, 12%, 18%, 28%) and the associated compensation cess regime.
These reforms rest on three key pillars:
1. Structural reforms – to resolve classification disputes, correct inverted duty structures, reduce litigation, and provide greater rate stability.
2. Rate rationalization – to reduce the tax burden on everyday essentials and aspirational goods, improving affordability and fueling consumption.
3. Ease of living – aimed at streamlining registration, enabling pre-filled returns, and accelerating refund processing—particularly for exporters and MSMEs.
The proposed GST rate rationalisation is set to benefit a wide range of products by reducing tax rates and simplifying slabs. Major gainers are expected to include consumer durables like air conditioners, automobiles, mobile phones, packaged foods and beverages, tractors and farm equipment, insurance premiums, footwear, apparel, building materials, and everyday essentials such as tea and milk products.
Potential Beneficiaries
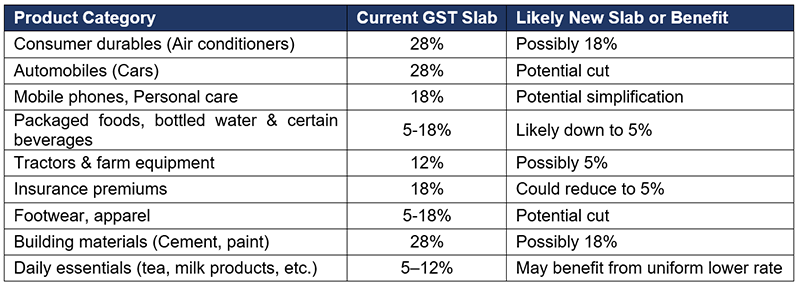
The new rate structure is expected to be formalized in the coming weeks, with proposals submitted to the Group of Ministers (GoM) and deliberations via the GST Council, with the goal of implementation by Diwali (23rd October).
View
This is a major reform and an unexpected positive surprise. We view these reforms as both timely and strategic. They are anticipated to boost domestic consumption and improve ease-of-doing-business, while offering a buffer against the recent global trade shocks.
These reforms also represent an ambitious effort to transform India’s indirect tax architecture into a simpler, more equitable, and growth-oriented system—delivered at a moment when reaffirming economic resilience and promoting affordability has become especially critical.
The recent phase of subdued economic growth may have been a key catalyst for the reforms announced today, though these measures come with fiscal implications. The proposed rationalization of GST rates is expected to result in lower indirect tax collections, potentially exerting some pressure on the fiscal position. Nevertheless, with the fiscal deficit having declined to 4.8% in FY25 and targeted at 4.4% for FY26, the government appears to have sufficient fiscal space to implement such reforms to support growth.

Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Facebook
Twitter
pintrest
instagram
Whatsapp
Linkedin
More