
CIO comments on Union Budget FY23
#
2nd Feb, 2022
- 6759 Views
NDNC disclaimer: By submitting your contact details or responding to Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited., with an SMS or Missed Call, you authorise Bajaj Allianz Life Insurance Company Limited and/or its authorized Service Providers to verify the above information and/or contact you to assist you with the purchase and/or servicing
This is a capex oriented budget with great emphasis on promoting domestic manufacturing and building infrastructure and also expanding the new age digital and technology sectors. The government has significantly increased the capital expenditure budget to Rs. 7.5 Lakh Cr. in FY23 while keeping the fiscal deficit target to 6.4% of GDP, which will support the economy over a longer period and also encourage private investments.
Focus on Capital Expenditure: Centre’s capex spending is expected to increase by 41.4% YoY in FY22RE to Rs. 6.02 Lakh Cr. against 27% YoY increase seen in FY21. Even in FY23, capex is expected to further increase by 24.5%. This year’s budget has focused on improving the investment demand, through enhanced public spending on infra which would crowd in private investment. On the other hand, revenue spending growth is expected to ease, noting only 2.7% increase in FY22RE to Rs 31.7 Lakh Cr. compared with 31.2% increase in FY21. Even in FY23, revenue spending is estimated to increase by only 0.9%. Hence, consumption demand would still be a laggard in FY23.
Higher than estimated FY22 Fiscal Deficit – The revised fiscal deficit target for FY22 is now at 6.9%, higher than the budgeted estimate of 6.8%. This is mainly owing to higher than projected for both revenue spending and capex. Government has increased the revenue and capex expenditure upwards by Rs. 2.4 Lakh Cr. and Rs. 0.5 Lakh Cr. respectively in FY22 revised estimates. Robust revenue collections, supported by rebound in economic activity have allowed fiscal slippage to be minimal. Centre’s tax revenues are expected to rise by 23.8% in FY22RE to Rs. 17.7 Lakh Cr. from budgeted estimate of Rs. 15.5 Lakh Cr. Non-tax revenues are also expected to overshoot the BE by Rs 70,000 Cr, while capital receipts are estimated to miss the target by Rs. 88,000 Cr. Due to lower than anticipated disinvestment proceeds. Hence, total receipts are expected to come in Rs 2.0 Lakh Cr. higher than the BE at Rs 21.8 Lakh Cr. Fiscal deficit target for FY23 (BE) at 6.4% is higher than market expectations (6-6.25%).
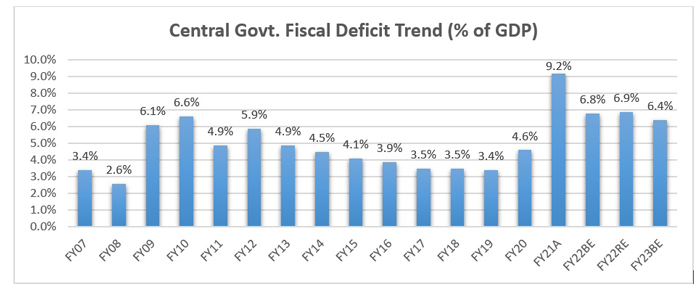
Source: Budget Documents. A= Actual, BE=Budgeted Estimate, RE = Revised Estimate
Higher Fiscal deficit to put pressure on yield: In FY23BE, gross borrowing is estimated at Rs 14.3 Lakh Cr. against Rs 10.47 Lakh Cr. in FY22RE. Even repayments are likely to be higher at Rs 3.2 Lakh Cr. compared to Rs 2.7 Lakh Cr. in FY22RE. Thus, net borrowing amounts to Rs 11.19 Lakh Cr., far higher compared to Rs 7.76 Lakh Cr. in FY22RE. Interest cost is also likely to be elevated at Rs 9.4 Lakh Cr. in FY23BE against Rs 8.14 Lakh Cr. in FY22RE. Hence, the growing debt burden and expansive borrowing program will put pressure on yields.
Taxation:
• There has not been much change in personal income tax slabs and rates and also corporate tax rates. The surcharge on LTCGs for all of the assets has been streamlined at 15%.
• Tax incentives initiated in 2019 for new manufacturing units at 15% rate has been extended by one more year. The tax incentives for the startup ecosystem has been extended by one year. This would further help in boosting domestic manufacturing and startup ecosystem.
• Scheme for taxation of Virtual Digital Asset: 30% (No deduction of expenses & set off available except for cost of acquisition). This will harmonize the trading of the digital assets.
Other key measures and figures announced in budget:
• Divestment target kept at Rs 65,000 Cr. for FY23 vs Rs1.75 Lakh Cr. for FY22 (BE) and Rs. 78,000 Cr. for FY22 (RE). The divestment targets now appear realistic given the privatization pipeline.
• Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) has been extended to March 2023 to provide much-needed additional credit to more than 130 lakh MSMEs. There has been additional amount of Rs. 50,000 Cr. earmarked exclusively for the hospitality and related enterprises which are severely hit due to the lockdowns. This will help the flow of credit to MSME sector and also banking sector in healthy assets loan growth.
• PLI:- Production linked incentive scheme, which has been a good success in boosting manufacturing gets further impetus through additional allocation of Rs19,500cr specifically targeted for solar modules manufacturing.
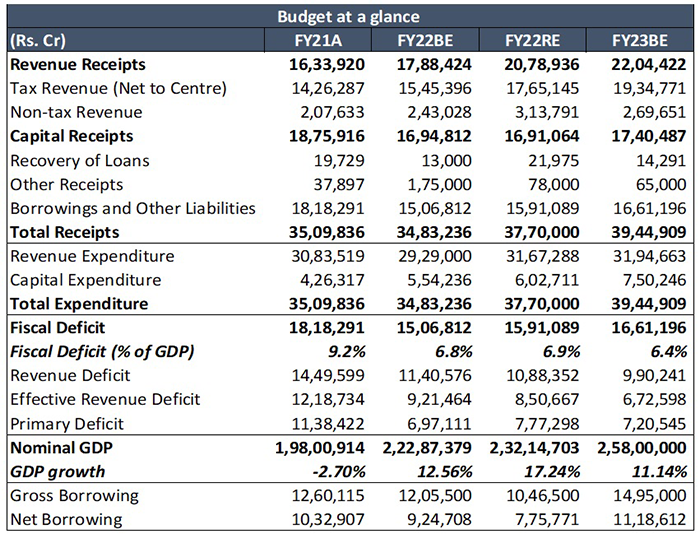
Source: Budget Documents. A= Actual, BE=Budgeted Estimate, RE = Revised Estimate
Outlook: The equity markets have cheered the budget with it being growth oriented, however, the bond markets have seen some hardening in yields due to the higher than expected fiscal deficit and government borrowing. The market will soon digest the budget and move on to fundamental factors and global cues. Corporate earnings in Q3 FY22 have been in line with the expectations and is expected to see moderate growth in FY22. Even though market valuations are elevated, the recovery in corporate earnings and the easy liquidity scenario globally may help to support valuations for some time. Overall, FY23 will be the year of normalization (from the Covid-19 pandemic) and will set the stage for acceleration in future growth.
Disclaimer:The views expressed by the Author in this article/note is not to be construed as investment advice and readers are suggested to seek independent financial advice before making any investment decisions. For any tax specific queries/clarifications, please contact your tax advisor. For more details please refer to the budget document and Finance Bill.”

Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Facebook
Twitter
pintrest
instagram
Whatsapp
Linkedin
More